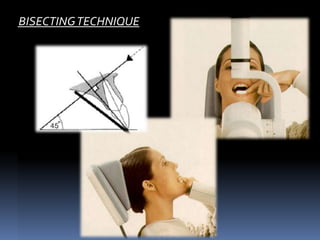
Further condensation may be carried out if required. Film and sensor placement Paralleling and bisecting the angle.
Periapical Radiography Pocket Dentistry
Participants will learn the intra-oral and extra-oral techniques and safeguards of dental radiology.
. A record peri-apical X-ray after delivery of the final prosthesis is necessary at this point. Prophylaxis paste and cup 4. However the anatomy of the oral cavity makes it.
Root canal pluggers may be used to condense the filling material into the canals. A thick mix of the treatment paste should then be prepared rolled into a point and carried into the canal. A periapical radiograph along the long axis of the implant is necessary to ensure that the abutment is seated.
Furthermore we will be free to use any ideas concepts know-how or techniques contained in any communication you send to us for any purpose whatsoever including but not limited to developing manufacturing and marketing products using such information. Light-bodied impression material dispenser 3. At this time the indications for CBCT examinations are not well developed.
20-gauge needle usually used for upper-tooth injections. Characteristics and qualities of the X-ray tube and the beam. Panoramic x-ray of full mouth.
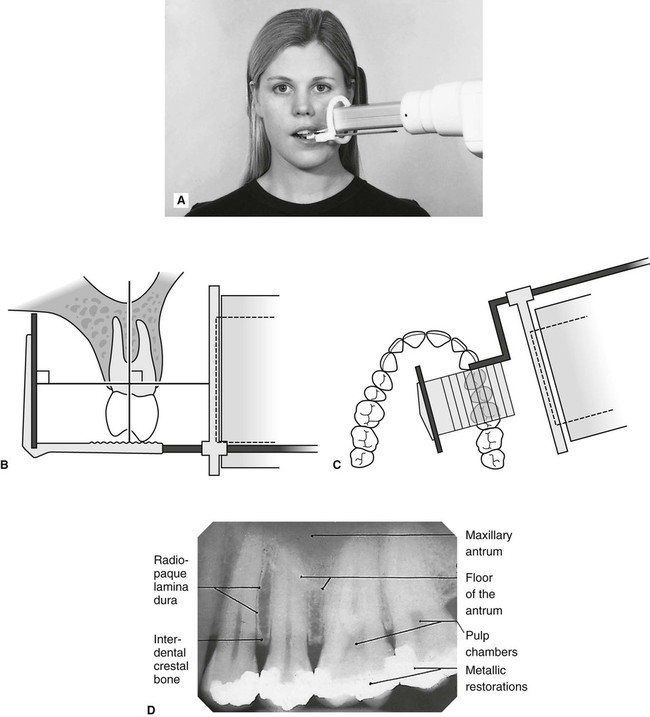
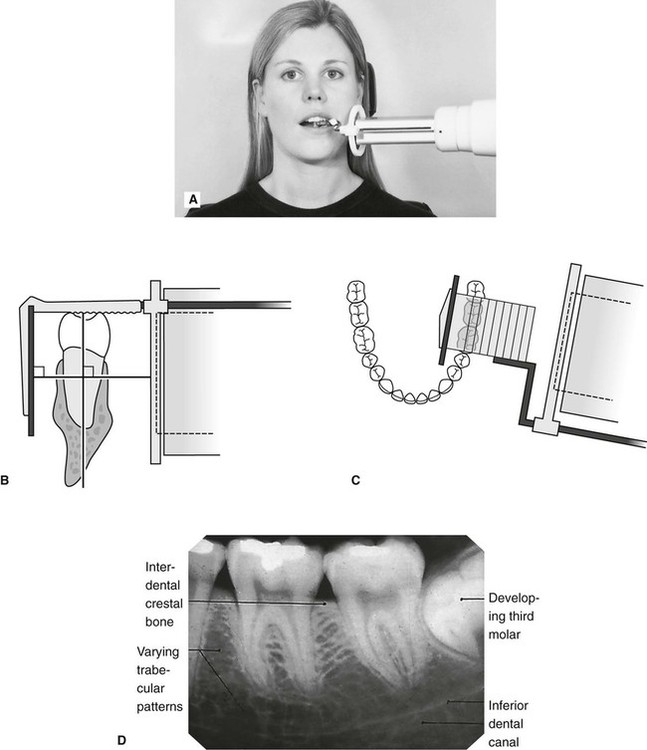
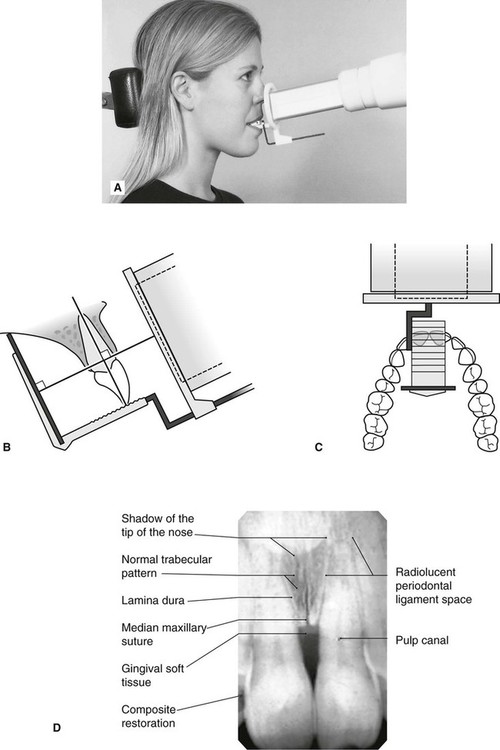
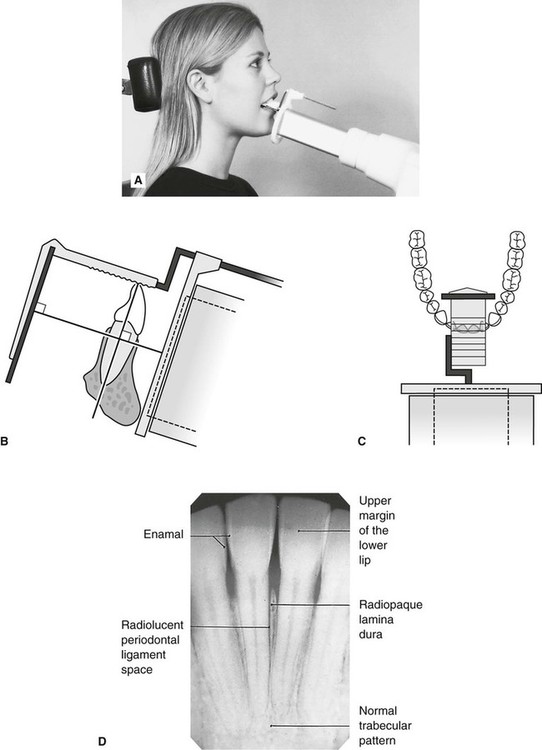
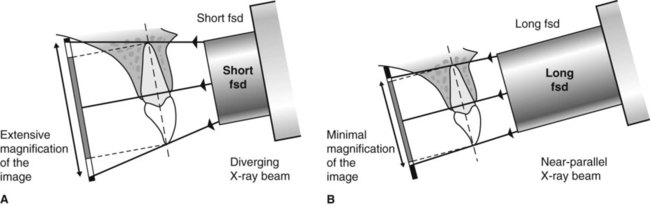
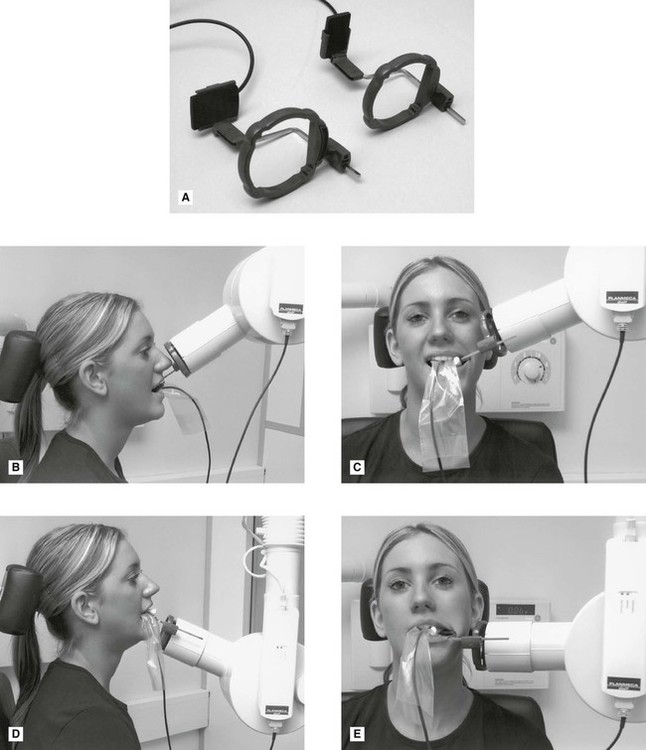
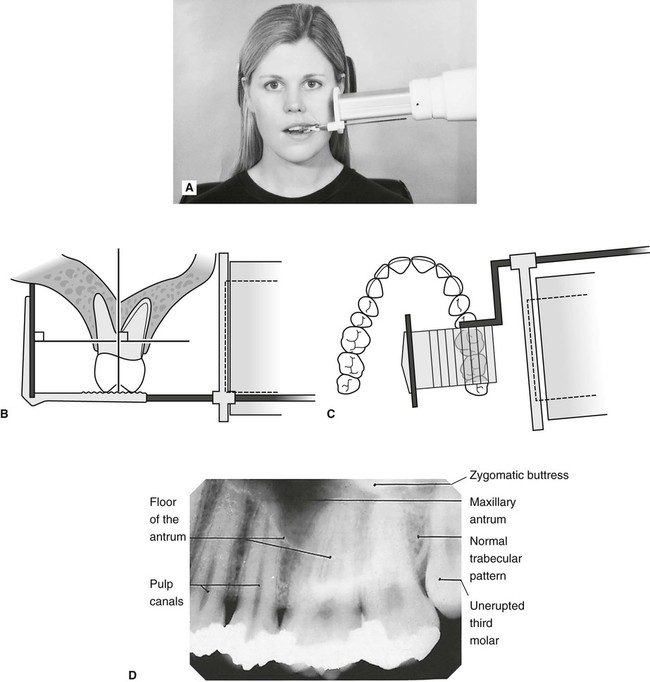
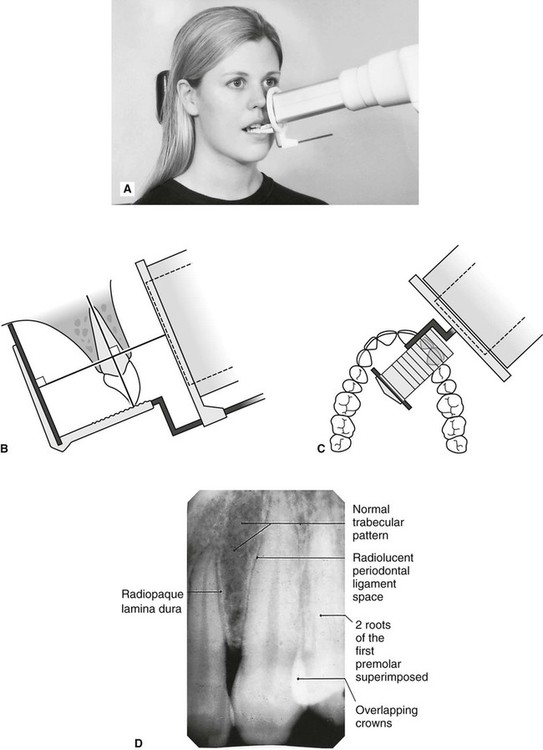
24-gauge needle usually used for lower tooth injections. Intra-oral radiographic techniques. The tooth under investigation and image receptor should be in contact or as close together as possible.
Production and properties of X-rays. Aspirator and suction tips 10. Selection of the radiographic techniques.
Periapical x-ray of one tooth. The X-ray beam from the tube-head should meet the tooth and the image receptor at right angles in both the vertical and horizontal planes. Radiation biology and protection.
Positioning should be reproducible. The ADA Council on Scientific Affairs has developed a statement on use of CBCT1 INTRODUCTION The guidelines titled The. Disposable saliva ejector and control pads 5.
The next follow-up visit should not exceed 4. This document deals only with standard dental imaging techniques of intraoral and common extraoral examinations excluding cone-beam computed tomography CBCT. X-ray holder and film 2.
This radiograph will be useful for follow-up and maintenance comparisons of bone level with later radiographs Figures 25a- -c. Dental probes and scalers 12. Different techniques and instruments are used to drain and decompress large periapical lesions ranging from placing a stainless steel tube into the root canal exhibiting persistent apical exudation 202 204 which is non-surgical decompression to placing polyvinyl or polyethylene tubes through the alveolar mucosa covering the apical lesion which is surgical.
Shimstock occlusal registration paper and holder 11. Fluoride given to children and adults after a prophy. SCS Screwdrivers long and short 7.
The patients oral hygiene. Jurisdiction Any dispute arising from these terms will be resolved exclusively in the state and federal courts of. An x-ray film may be necessary to allow evaluation of the success in filling the canals Fig.
Periapical Radiography Pocket Dentistry
Periapical Radiography Pocket Dentistry
Periapical Radiography Pocket Dentistry
Periapical Radiography Pocket Dentistry

Periapical Radiography Pocket Dentistry
0 comments
Post a Comment